- Room Number 05, Ground Floor, OPD Block Fortis Hospital Mohali Phase 8, Sector 62, Punjab.
Other Treatments
dementia
Dementia is a collective term for cognitive decline that interferes with daily life, affecting memory, thinking, and social abilities. It’s caused by brain cell damage from conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, Lewy body dementia, and frontotemporal disorders. Symptoms include memory loss, confusion, difficulty with communication, impaired judgment, and personality changes. Diagnosis involves medical history, cognitive tests, neurological exams, and brain imaging. While there’s no cure, treatments focus on managing symptoms, slowing progression, and improving quality of life through medications, lifestyle changes, and supportive therapies. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for better management.


seizures
Seizures are sudden, uncontrolled electrical disturbances in the brain, causing changes in behavior, movements, feelings, or consciousness. They can be focal (affecting one part of the brain) or generalized (affecting the whole brain). Symptoms range from staring spells and confusion to convulsions and loss of consciousness. Causes include epilepsy, brain injuries, infections, tumors, and genetic factors. Diagnosis involves medical history, neurological exams, EEGs, and brain imaging. Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may include antiepileptic medications, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgery. Proper management aims to control seizures and minimize their impact on daily life.
movement disorder
Movement disorders are a group of conditions characterized by abnormal, involuntary, or impaired voluntary movements. They include disorders like Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, dystonia, and Huntington’s disease. Symptoms can range from tremors and muscle rigidity to uncontrollable movements and impaired coordination. These disorders may arise from genetic factors, brain injuries, or degenerative diseases affecting the basal ganglia and other brain regions responsible for movement control. Diagnosis involves neurological evaluations, patient history, and imaging studies. Treatment aims to manage symptoms and improve quality of life through medications, physical therapy, and sometimes surgical interventions, depending on the specific disorder.


tremor
A tremor is an involuntary, rhythmic shaking or oscillation of a body part, often affecting the hands, arms, or head. It can be caused by various conditions, including essential tremor, Parkinson’s disease, or multiple sclerosis, and can also result from anxiety or fatigue. Tremors may occur at rest, during movement, or in specific postures, depending on the underlying cause. They can range from mild to severe, impacting daily activities and quality of life. Diagnosis involves medical history, neurological examination, and sometimes imaging or blood tests. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms with medications, physical therapy, and, in some cases, surgery.
Ataxia
Ataxia is a neurological condition characterized by a lack of muscle coordination, leading to unsteady movements and difficulties with balance, walking, and fine motor tasks. It can result from damage to the cerebellum, spinal cord, or peripheral nerves, often due to genetic disorders, stroke, multiple sclerosis, or head injury. Symptoms include clumsiness, tremors, difficulty with speech and swallowing, and abnormal eye movements. Diagnosis involves medical history, neurological exams, and imaging tests. While there is no cure, treatment aims to manage symptoms and improve quality of life through physical therapy, occupational therapy, and addressing underlying causes.


Imbalance
A tremor is an involuntary, rhythmic shaking or oscillation of a body part, often affecting the hands, arms, or head. It can be caused by various conditions, including essential tremor, Parkinson’s disease, or multiple sclerosis, and can also result from anxiety or fatigue. Tremors may occur at rest, during movement, or in specific postures, depending on the underlying cause. They can range from mild to severe, impacting daily activities and quality of life. Diagnosis involves medical history, neurological examination, and sometimes imaging or blood tests. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms with medications, physical therapy, and, in some cases, surgery.
neuropathy
Neuropathy, or peripheral neuropathy, refers to damage to the peripheral nerves, causing weakness, numbness, and pain, typically in the hands and feet. It can result from diabetes, infections, traumatic injuries, metabolic problems, or exposure to toxins. Symptoms include tingling, burning pain, sharp, jabbing sensations, muscle weakness, and sensitivity to touch. Diagnosis involves physical exams, neurological assessments, blood tests, and sometimes nerve conduction studies or electromyography. Treatment focuses on managing the underlying cause, relieving symptoms through medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes, and preventing further nerve damage to improve the patient’s quality of life.

myopathy
Myopathy refers to diseases of the muscle tissues that result in muscle weakness, cramps, stiffness, and spasms. Causes include genetic factors (like muscular dystrophies), metabolic disorders, inflammation (such as polymyositis), and drug-induced or toxic myopathies. Symptoms often involve progressive muscle weakness, particularly in the proximal muscles (those closest to the body’s center). Diagnosis involves clinical examination, blood tests (for elevated muscle enzymes), electromyography (EMG), muscle biopsy, and genetic testing. Treatment depends on the specific type of myopathy and may include medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments to manage symptoms and improve muscle function and quality of life.
numbness
Numbness is a loss of sensation or a feeling of pins and needles in a part of the body, often the hands, feet, arms, or legs. It can result from nerve compression, injury, or underlying conditions such as diabetes, carpal tunnel syndrome, multiple sclerosis, or peripheral neuropathy. Symptoms include reduced ability to feel touch, pain, or temperature changes. Diagnosis involves medical history, physical examination, and tests like nerve conduction studies, electromyography (EMG), and imaging. Treatment focuses on addressing the underlying cause, relieving symptoms through medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes, and preventing further nerve damage.
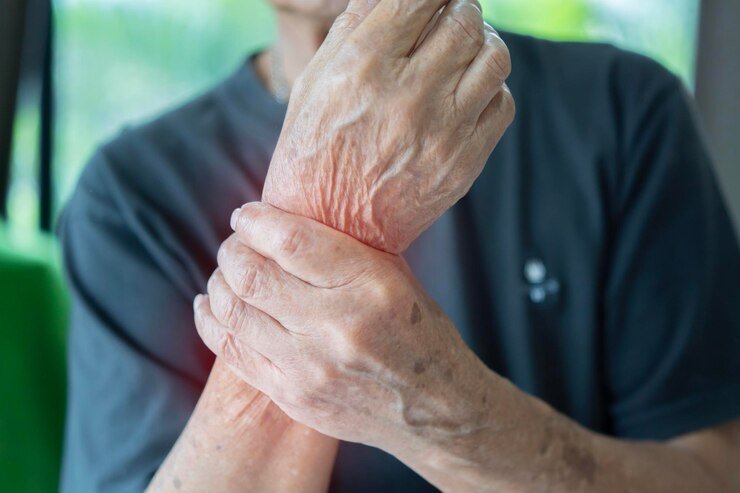

cervical Spondylosis
Cervical spondylosis is age-related degeneration of the cervical spine (neck), involving the intervertebral discs and vertebrae. It commonly results in symptoms like neck pain, stiffness, and sometimes radiating pain or numbness in the shoulders, arms, and hands due to nerve compression. Other symptoms can include headaches and reduced range of motion in the neck. Diagnosis involves physical exams, imaging tests like X-rays, MRI, or CT scans. Treatment options include pain relief through medications, physical therapy to improve flexibility and strength, lifestyle changes, and, in severe cases, surgical intervention to relieve nerve compression and stabilize the spine.
lumbar Spondylosis
Lumbar spondylosis is the degeneration of the lumbar spine (lower back), typically associated with aging. It involves the wear and tear of intervertebral discs, vertebrae, and facet joints. Symptoms include lower back pain, stiffness, and sometimes radiating pain, numbness, or weakness in the legs due to nerve compression (sciatica). Diagnosis involves a physical exam and imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans. Treatment focuses on pain management with medications, physical therapy to strengthen and improve flexibility, lifestyle modifications, and, in severe cases, surgical options to relieve nerve compression and stabilize the spine.
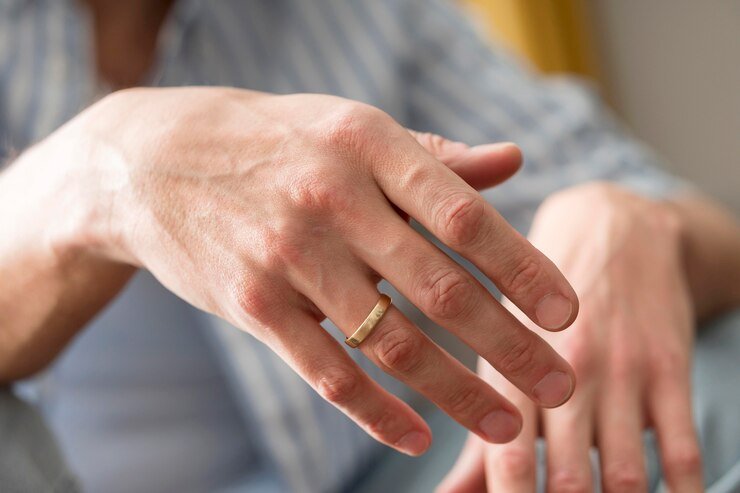

dystonia
Dystonia is a neurological movement disorder characterized by involuntary muscle contractions, leading to repetitive movements or abnormal postures. These contractions can affect a single muscle, a group of muscles, or the entire body. Symptoms vary widely but often include twisting, tremors, and abnormal postures, which can be painful and interfere with daily activities. Causes include genetic mutations, brain injuries, infections, or exposure to certain medications. Diagnosis involves clinical examination, patient history, and sometimes genetic testing or brain imaging. Treatment options include medications, physical therapy, Botox injections to relax affected muscles, and, in severe cases, deep brain stimulation (DBS).
chorea
Chorea is a neurological disorder characterized by involuntary, rapid, and unpredictable muscle movements that flow from one part of the body to another. These movements can affect the face, hands, feet, and other body parts, leading to difficulties with coordination and performing voluntary actions. Causes include genetic conditions like Huntington’s disease, infections, autoimmune diseases, and certain medications. Symptoms may also include muscle weakness and cognitive or emotional disturbances. Diagnosis involves clinical evaluation, family history, and imaging or genetic tests. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms through medications, physical therapy, and addressing the underlying cause to improve the patient’s quality of life.
hemiballismus
Hemiballismus is a rare movement disorder characterized by violent, involuntary, and irregular flinging movements of one side of the body, typically affecting the arm and leg. These movements result from damage to the subthalamic nucleus in the brain, often due to a stroke, tumor, or infection. Symptoms can be severe and interfere with daily activities. Diagnosis involves clinical evaluation, patient history, and imaging studies like MRI or CT scans to identify underlying brain abnormalities. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms with medications such as antipsychotics or anticonvulsants, and in some cases, surgical intervention may be considered to control the movements.
multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the protective myelin sheath covering nerve fibers in the central nervous system. This results in communication problems between the brain and the rest of the body. Symptoms vary widely and can include fatigue, difficulty walking, numbness, muscle weakness, vision problems, and cognitive issues. The cause of MS is unknown, but it involves a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Diagnosis is based on medical history, neurological exams, MRI scans, and sometimes spinal fluid analysis. While there is no cure, treatments focus on managing symptoms and slowing disease progression.
demyelinating disorder
Demyelinating disorders are conditions in which the myelin sheath, the protective covering around nerve fibers, is damaged or destroyed. This impairs the nerve’s ability to transmit electrical signals, leading to a range of neurological symptoms. Common demyelinating disorders include multiple sclerosis, neuromyelitis optica, and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Symptoms can include muscle weakness, numbness, vision problems, coordination difficulties, and cognitive impairments. Diagnosis typically involves medical history, neurological examinations, MRI scans, and sometimes lumbar punctures. Treatment aims to manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and slow disease progression through medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments.
Brain infections
Brain infections involve inflammation and damage to brain tissue caused by microorganisms like bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. Common types include meningitis (infection of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord), encephalitis (inflammation of the brain itself), and brain abscesses (localized infections forming pus-filled cavities). Symptoms may include headache, fever, seizures, altered consciousness, and neurological deficits. Diagnosis involves medical history, physical exams, imaging studies (CT or MRI), and sometimes lumbar punctures or blood tests. Treatment varies based on the infection’s cause and may include antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal medications, and supportive care to manage symptoms and prevent complications.